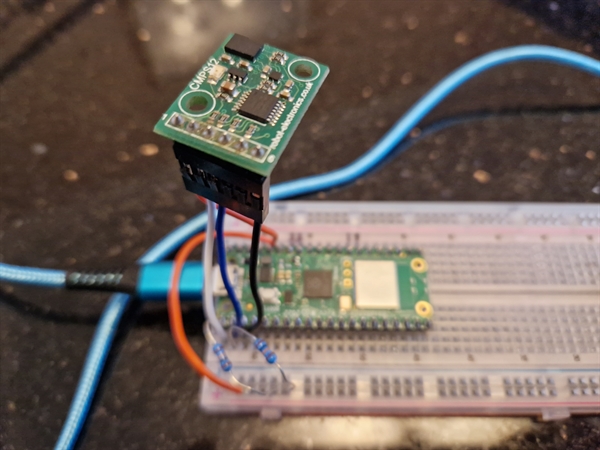
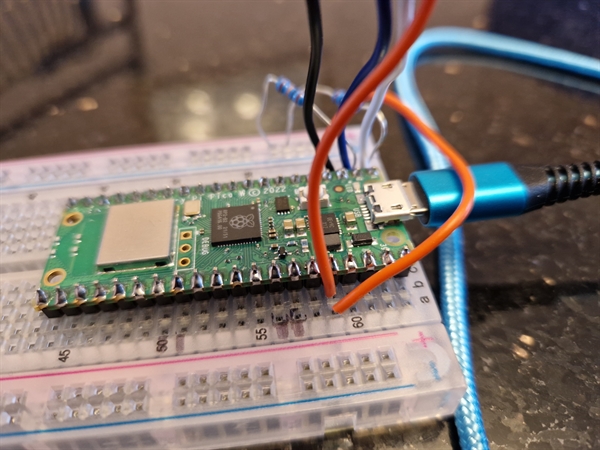
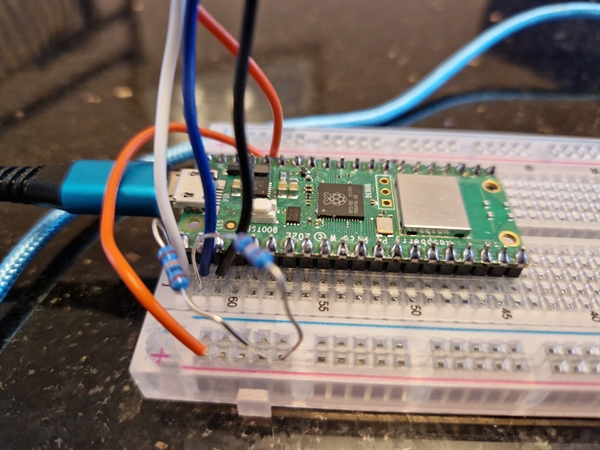
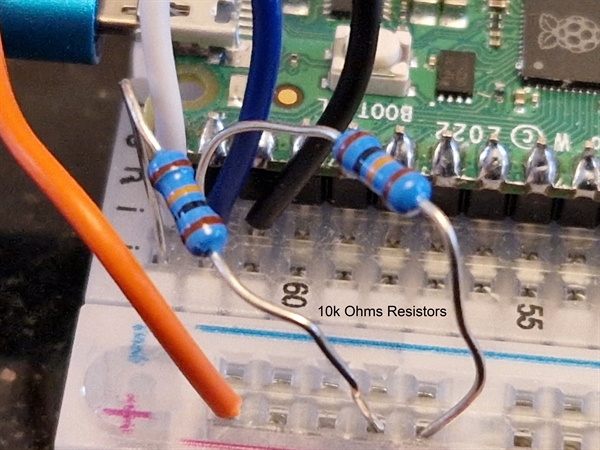
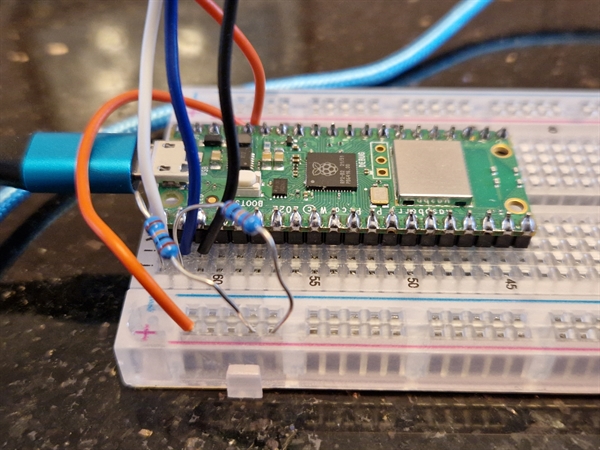
Raspberry Pi Pico W with CMPS12 compass
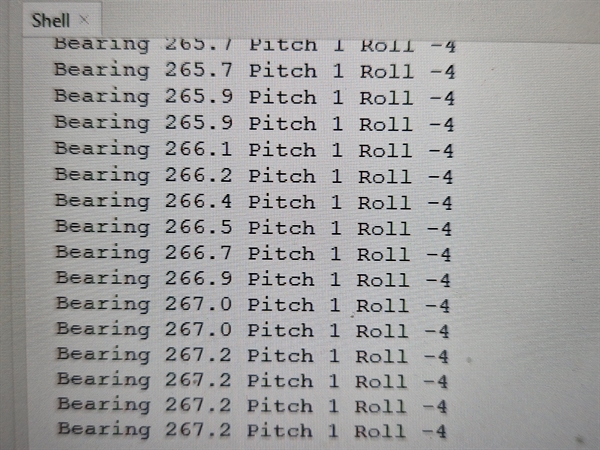
Example code of connecting the Raspberry Pi Pico W to a CMPS12 digital compass.
Connections
| Description | Colour | Pico W | CMPS12 compass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power 3v | Orange | pin36 3V3(OUT) | 3.3v |
| Ground | Black | pin3 GND | GND |
| i2c Data | White | pin1 GP0 i2c0 SDA | Second from top |
| i2c Clock | Blue | pin2 GP1 i2c0 SCL | Third from top |

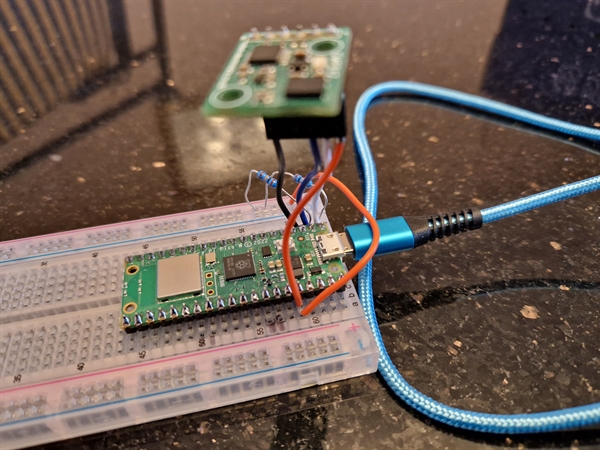
Photo